Learning about body parts of chicken or chicken external anatomy is very important. Different chicken breeds contain some special characteristics. And the the characteristics of different body parts of chicken contain the behavior of different generation of chicken.
If you want to raise chicken commercially, then you must have to know about the characteristics of different body parts of chicken. Meat and egg of chicken are very necessary and popular human food. Meat and egg production of chicken highly depends on their body size and structure.
So, it is very important to have good knowledge about external and internal body parts of chicken with the introduction of their breeds. Because we can define productive and non-productive breeds by their body size and parts.
For example- different types of chicken breeds have different sized and colored comb in their head. Some breeds contain single comb, some have rose comb and some breeds with pea comb.
Similarly ear lobe, feather, skin, wings etc. also are of different types of various breeds. So, body parts of chicken helps to know about that breed and their variant. We can also determine healthy and unhealthy chicken by following the body parts of chicken.
Why Learning Body Parts of Chicken Important?
Learning the body parts of a chicken is very important, because it helps us to understand chicken external anatomy and how to take care of them. When we know their body parts, we can keep them healthy by checking for any problems. It also helps when you want to cook or prepare chicken because you can choose the right parts for your meals.
External Body Parts Of Chicken
Here we are trying to shortly describe different important external body parts of chicken. External body parts of a chicken is also called chicken external anatomy.

1. Comb
Comb is a small ice of meat above the chickens head. Various chicken has about 8 types of comb. In general we know about single comb, rose comb and pea comb. We can differentiate cock and hen by their comb. The comb of cock is slightly bigger than hen comb.

2. Nostril
The nostril of chicken is near on the joint place of beak and comb.

3. Beak
Beak of chicken is on the front side of head. It is very strong and suitable to collect crop from the ground.

4. Eye
The chicken has two bright eyes. We can identify if they are healthy or not by their eyes.
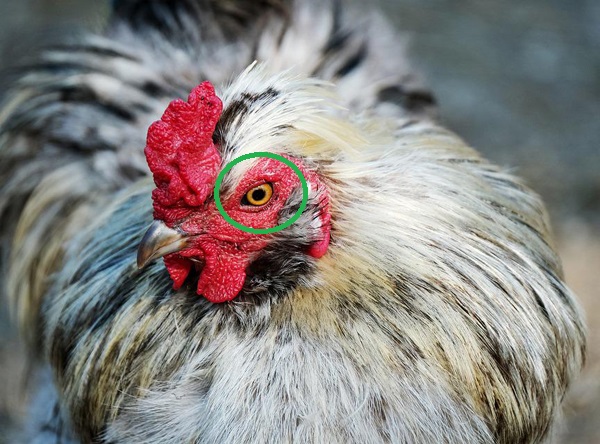

5. Ear Lobe
The hanging skin from chicken ear is known as ear lobe. There are various colored ear lobe of chicken. We can see light red, deep red and white colored ear lobe of chicken.
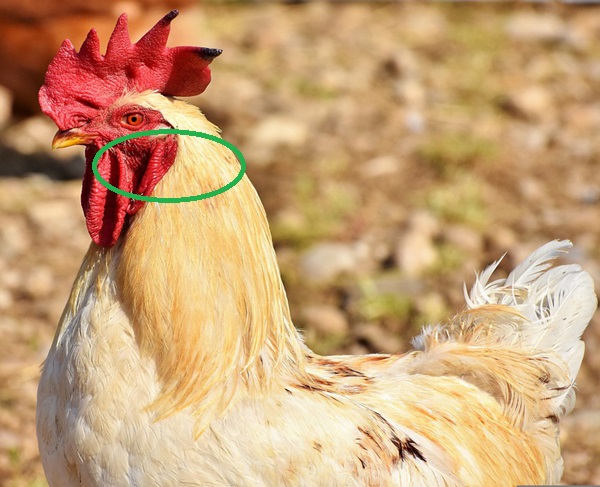

6. Wattle
The soft meat hanging from the two side of chicken beak is known as wattle. It is also of various colored.

7. Wing
The chicken has two wings. With those wings they can fly slightly. They have some feather in their wings which are suitable for flying. This feathers are known as primary feather. They have about 10 primary feather. We can’t see those if they do not spread their wings.

8. Tail
Both cock and hen has a tail. The feather of tail of cock get curved to down when it become big sized and it looks like a sickle. Hens are of different typed. So, we can differentiate between hen and cock by their tail.

9. Vent
Closet and eggs of chicken come out from the vent of chicken. Sperm also come out from the vent of chicken.
10. Leg
The chicken has a pair of leg and every leg contain four small and big sized claw.

Internal Body Parts of Chicken
Internal body parts of chicken consists of several key parts:
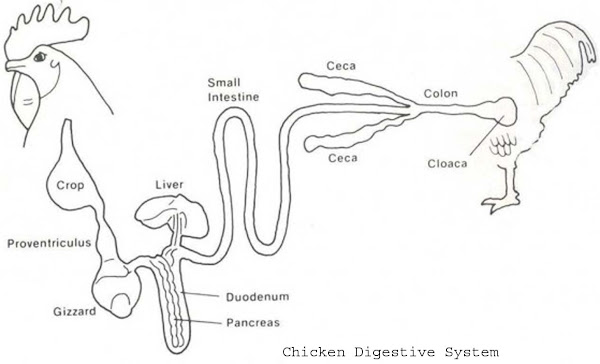
1. Digestive System
The digestive system of a chicken is responsible for breaking down food and extracting nutrients for growth and energy. Parts in a chicken’s digestive system are:
- Beak
- Crop
- Proventriculus
- Gizzard
- Small Intestine
- Ceca
- Large Intestine
2. Respiratory System
Respiratory system of a chicken is unique, and it includes lungs and air sacs.
3. Circulatory System
Chicken’s circulatory system transports oxygen and nutrients throughout their bodies. Parts in a chicken’s circulatory system are:
Heart: Like mammals, chickens have a small heart with four chambers. It pumps oxygenated blood to various parts of the body.
Blood Vessels: Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins bring deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that allow for nutrient and oxygen exchange within tissues.
4. Reproductive System
Chickens have a complex reproductive system that is different for roosters and hens.
Roosters: Roosters have testes, which produce sperm. They transfer sperm to the hen’s cloaca during mating, where fertilization occurs.
Hens: Hens have a pair of ovaries, where eggs are produced. The eggs move through the oviduct, where they are fertilized if a rooster is present, and then laid through the cloaca.
5. Excretory System
Chickens excrete waste through a combined opening called the cloaca.
Cloaca: The cloaca is a single opening where waste from the kidneys is eliminated from the body (as well as reproductive and digestive waste).
Kidneys: Chickens have small kidneys that filter waste from the bloodstream.
6. Nervous System
Compared to humans, chickens have a relatively simple nervous system. But it serves their needs.
Brain: The brain controls various functions, including movement, behavior, and sensory perception.
Nerves: Nerves transmit signals from the brain to muscles and organs, allowing chickens to move and react to their environment.
These are the body parts of a chicken. Hope this guide has helped you! Good luck!
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
People often ask questions related to chicken body parts. Here we are going to list the most common and frequently asked questions about body parts of chicken.
What part of the body is chicken gizzards?
The chicken gizzards are actually a part of the digestive system of a chicken. Chicken gizzards are muscular organs located just behind the liver in the gastrointestinal tract. Gizzards play a very important role in the digestive system, and helps to grind and crush food (as chickens do not have teeth to chew). Gizzards often contain small stones or grit that the chicken ingests to aid in their grinding process. However, in culinary uses, the chicken gizzards are considered a delicacy in many cuisines and are known for their unique taste, texture and flavor.
What are the body parts of a chicken?
Chicken body parts of a chicken are of two types, external and internal. We have already discussed about both above.
What body part do chicken eggs come from?
Like other domestic birds, the chicken eggs also come from the ovary of a hen. The eggs production process begins when the hen’s ovaries release an ovum (yolk). The ovum travels through the oviduct. As the yolk moves through the oviduct, layers of albumen (the white part of an egg), membranes, and the shell are added around it. And finally, the hen lay an completed egg through her vent (vent is the opening which is used for excretion and reproduction). The egg itself is not a body part, it is formed from several components within the hen’s reproductive system.
What part of the body do chicken tenders come from?
The chicken tenders come from the pectoralis minor muscle. It is located beneath the breast meat of the chicken. The muscle is sometimes referred to as the “tender” because it is small, tender strip of meat. The chicken tenders are typically boneless and skinless. That’s why they are a popular choice for frying, grilling, and baking. In some places, chicken tenders are often marketed as a separate cut due to their tenderness and flavor.







What are the function of the external part of the head of a cock
Read more about rooster coxcomb. Good luck!