Sheep farming can be a rewarding and profitable enterprise, but it also requires vigilance when it comes to sheep diseases. Sheep are susceptible to a wide range of diseases, some of which can be fatal if not detected and treated early. Here we will discuss some of the most common sheep diseases, their symptoms, and prevention and treatment measures.
The main prerequisite of getting desired production from any animal is controlling their diseases. Same disease preventive steps should take for diseases of sheep like other animal cow, goat, buffalo etc.
Diseases preventive methods of goat and sheep are about same. But as the sheep stay in group so, if one sheep get infected by any diseases the the whole group may affected.
And the probability of getting infected is very high. Parasites is very high in sheep than goat. Harmful insects can easily take place in the wool of sheep and do a lot of damage of the sheep.
This parasites can easily spread throughout the group. So, wash the sheep regularly with parasites removing medicine or spread this over their body.
Apply disease preventive vaccine according to the suggestion of veterinary surgeon to keep the sheep free from disease.
Feed the sheep worm protective medicine regularly to keep themselves free from worms like tapeworm, flatworm, roundworm etc.
Types Sheep Diseases
Sheep diseases are of various types. Here we are trying to describe more information about these. To prevent this diseases the farmer should take necessary steps according to the local veterinary surgeon.
- Prioners Disease
- Viral Diseases
- Bacterial Diseases
- Fungal Diseases
- Parasitic Diseases
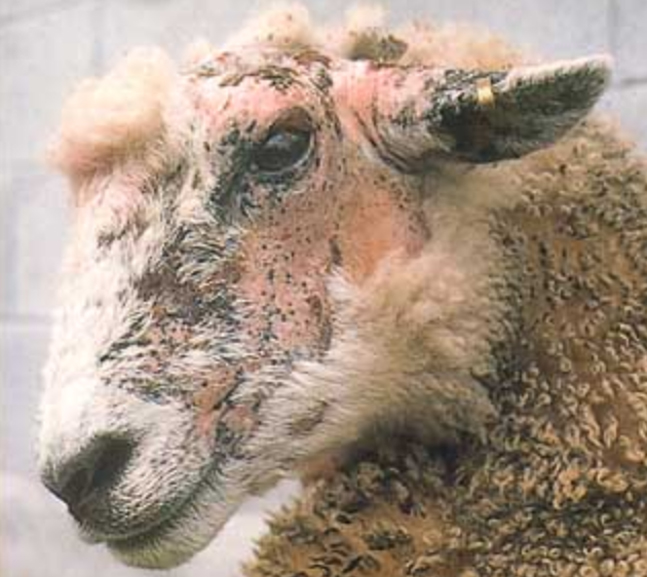
Common Sheep Diseases
Here we are shortly describing about the most common diseases of domestic sheep and their preventive methods.
Footrot
Footrot is a common bacterial disease that affects sheep’s hooves. It causes inflammation and damage to the soft tissue between the toes, leading to lameness, reduced appetite, and weight loss. The bacteria responsible for footrot thrive in wet and dirty conditions, so keeping the sheep’s living environment clean and dry is critical to preventing and controlling the disease. Treatment involves antibiotic therapy, foot trimming, and disinfecting the affected areas.
Parasitic Infections
Sheep are also prone to parasitic infections, particularly internal parasites such as roundworms and tapeworms. These parasites can cause diarrhea, anemia, weight loss, and even death if not treated promptly. Regular deworming, pasture management, and good hygiene practices can help prevent parasitic infections in sheep.
Scrapie
Scrapie is a fatal neurological disease that affects sheep and goats. It is caused by a prion, a type of abnormal protein, and can be transmitted from animal to animal. Scrapie can cause behavioral changes, such as increased nervousness and scratching, as well as weight loss and muscle tremors. Unfortunately, there is no cure for scrapie, and infected animals must be culled to prevent the spread of the disease.
Bluetongue
Bluetongue is a viral disease that is transmitted by midges. It affects sheep and other ruminants and can cause fever, respiratory problems, and lameness. In severe cases, bluetongue can lead to death. Vaccination and midge control measures can help prevent bluetongue from affecting sheep.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a respiratory disease that can affect sheep of all ages. It is caused by bacteria or viruses and can be transmitted through the air or by direct contact with infected animals. Pneumonia can cause coughing, fever, and difficulty breathing, and can be fatal if not treated promptly. Vaccination, good ventilation, and hygiene practices can help prevent pneumonia in sheep.
Orf
Orf, also known as contagious ecthyma, is a viral disease that affects sheep’s lips and mouth. It causes scabby sores that can be painful and interfere with feeding. Orf can also be transmitted to humans, so it is essential to handle infected animals with caution. Vaccination and good hygiene practices can help prevent the spread of orf in sheep flocks.






