Artificial insemination in cattle is a reproductive technology that has been used in cattle breeding for many years. It is shortly known as AI. It involves the insertion of semen from a male bull into the reproductive tract of a female cow. It is typically done by using a specialized catheter or syringe. The goal of artificial insemination in cattle is to breed large numbers of cows efficiently and effectively with high-quality semen from genetically superior bulls.
There are numerous benefits of artificial insemination in cattle. Top benefits include the rapid spread of superior genetics throughout a herd, reduced risk of disease transmission, and improved productivity and profitability.
The AI procedure is quick and painless for the cow and can be performed by a trained technician or veterinarian. After insemination, you have to monitor the cow for pregnancy and can be inseminated again during her next estrus cycle if needed. However, artificial insemination in cattle is a safe and effective way to breed cattle.
What Is Artificial Insemination In Cattle?
Artificial insemination in cattle is a breeding technology that involves the artificial introduction of semen into the reproductive tract of a cow for the purpose of fertilization. This process is typically used in commercial farms for cow breeding to produce offspring with desired traits or to improve the genetics of a herd or population.
Artificial insemination in cattle can be performed manually, using a syringe or catheter to introduce the semen, or with the use of specialized equipment and techniques. The benefits of artificial insemination include improved efficiency and productivity in breeding programs, as well as reduced risk of disease transmission compared to natural breeding.
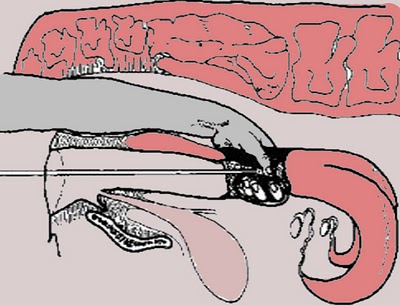
Benefits of Artificial Insemination In Cattle?
Top benefits of artificial insemination in cattle are:
- Genetic improvement
- Increased efficiency
- Reduced risk of disease
- Improved animal welfare
- Increased access to genetics
Preparation For Artificial Insemination in Cattle
Preparation for artificial insemination is essential to ensure the success of the procedure. And it is also essential to ensure the health and safety of the cattle. Select the right bulls for breeding based on their genetics, performance and overall health conditions. The cows should also be very healthy and active. And prepare the required equipment for AI such as insemination guns, catheters, semen straws, and gloves. Clean, disinfect and store the equipment properly to avoid contamination.
Handle the semen with care to maintain it’s fertility and viability. Use only high-quality semen from a reputable source and store it in liquid nitrogen until it is ready to be used. Perform the insemination procedure by a trained technician or veterinarian. Restrain the cow properly to minimize stress and ensure safety. Insert the insemination gun or catheter carefully into the reproductive tract. And deposit the semen at the appropriate location.







We use AI for breeding our cows. We have only 3 cows with few calves. Keeping a bull costs much for smaller farms like ours. So AI is best option for us.
Yes, AI is the best option for small farmers with few cows. It helps to reduce the cost of raising a bull. Good luck!